Foamy urine can be an early indicator of kidney disease and depending on the severity of a particular case, different parameters may be looked at such as stages and aetiological factors defining kidney injury. In Ayurvedic terms, foamy urine indicates an imbalance of mutravaha srotas, or the urinary system, and possible disturbance in one of the doshas, particularly Kapha and Pitta.
This may be seen more or less in the stage where kidney disease has begun to set in but may begin by indicating mild to moderate proteinuria, which is the condition where the kidneys are beginning to lose excess protein in the urine.
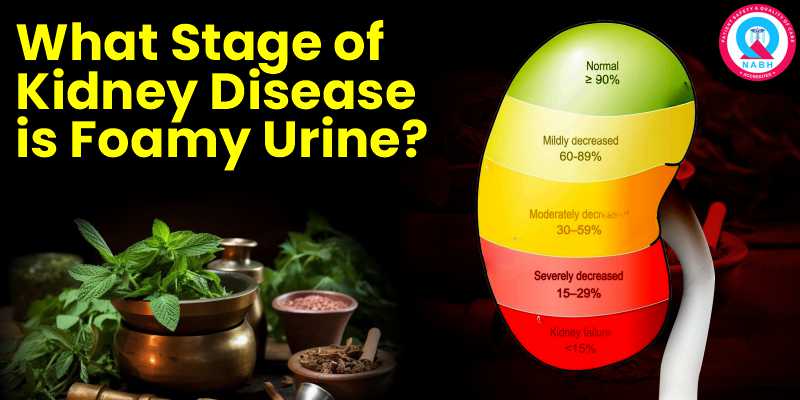
Kidney disease has been graded according to the rate of glomerular filtration (GFR) into 5 stages that reflect how well the kidney filters wastes.
Foamy urine is typically characteristic of Stage 1 to Stage 3, but it can, however, occur even at more advanced stages. Let's take a close look at this progression by way of Ayurveda.
According to Ayurveda, this stage indicates an imbalance of Pitta dosha, characterized by overheating or inflammation of the mutravaha srotas. The first occurrence of Ama (toxins) builds up in the body and interferes with proper filtration.
Symptoms include intermittent foamy urine that may be accompanied by mild feelings of fatigue or dehydration.
Ayurvedic Management: The emphasis of treatment should start with Pitta pacification with the removal of Ama using cooling herbs like Amla, Guduchi, and dietary changes.
As per Ayurvedic interpretation, Kapha is primarily aggravating to obstruct the proper channels of kidneys. The ama increases, revealing the blockade effect of filtration processes.
Symptoms at this stage include persistent foamy-slimy urine with mild swelling (edema) in the hands or feet. The thirst might be excessive.
Herbs: Diuretics and tonics for kidneys like Punarnava, Gokshura, and Varunadi Kwath should be used for cleansing and supporting kidney function.
Diet: Avoid heavy, salty, or processed foods. Light, Kapha-pacifying food should be preferable: barley, pomegranate, and bitter vegetables.
Lifestyle: Gentle yoga (like Bhujangasana) and meditation enhance circulation and detoxification.
As per Ayurvedic interpretation, both Kapha and Vata aggravate the stage. The dryness and hardening of urinary channels further block filtration. Pitta continues to provoke inflammation at stage 3.
Symptoms will be more prominent and foamy urine is accompanied by fatigue, mild anemia, and elevated blood pressure.
Chandraprabha Vati: A classical Ayurvedic formulation that helps to balance out the doshas and thus improves urinary health.
Ashwagandha: Energy and amenity to meet.
Panchakarma therapy, including Virechana, may work in conjunction with proper liquid intake to quicken Ama clearance and improve the doshas.
Warm herbal teas made from coriander or fennel seeds can be consumed by the patient.
Foamy urine in Ayurveda usually denotes early to moderate kidney complaints, which may be linked with dosha imbalances, Ama accumulation, and protein leak. Ayurvedic management mainly looks toward clearing the root cause through herbal remedies, detoxification, and lifestyle modification.
Choose Karma Ayurveda is best ayurvedic treatment in India, for an improved quality of life. Contact us now to learn more about ayurvedic treatment for proteinuria, Panchakarma therapies, and other such things.
Second Floor, 77, Block C, Tarun Enclave, Pitampura, New Delhi, Delhi, 110034